Permaculture: Mimicking Nature's Wisdom
Overview
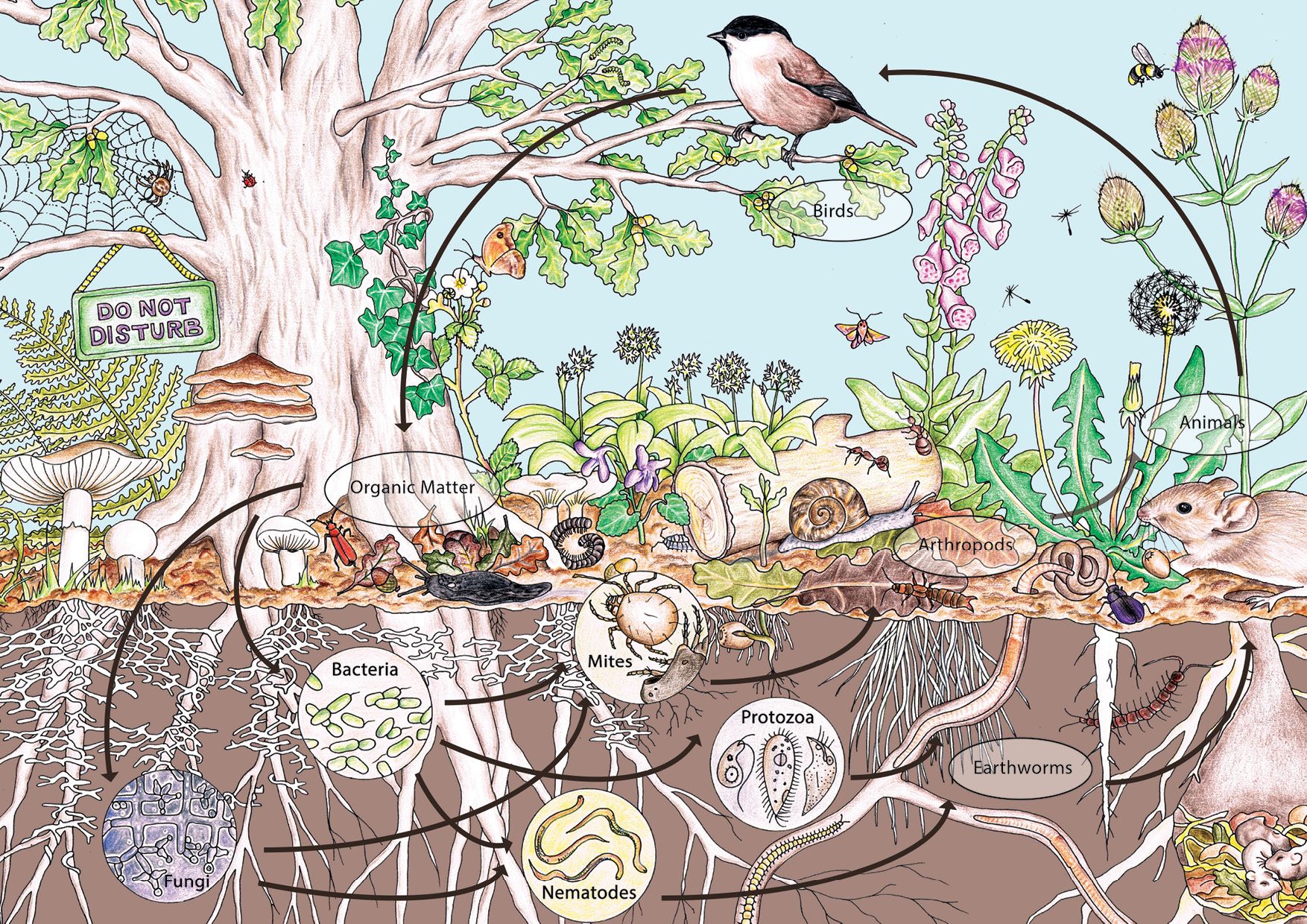
In the realm of sustainable agriculture, permaculture stands as a beacon of holistic land management and design. Its essence lies in replicating patterns and relationships found in natural ecosystems to foster sustainability, resilience, and biodiversity.
History and Evolution
Conceived in the 1970s by the visionary Australian, Bill Mollison, and his diligent student, David Holmgren, permaculture has transitioned from an agricultural methodology to an ecological philosophy that embodies a worldwide grassroots movement. This transition represents a shift towards a more symbiotic relationship with the environment, emphasising waste reduction, pollution prevention, and wildlife protection.
Philosophy and Principles
Permaculture extends beyond mere agricultural practices, evolving into a life philosophy that promotes harmony with nature. This approach advocates for the utilisation of patterns observed in natural ecosystems to enhance the land's resilience and biodiversity, paving the way for a more sustainable and harmonious future.
Aquaponics: A Harmonious Food Production System
Overview
In the innovative field of food production, aquaponics emerges as a synergistic system that integrates aquaculture and hydroponics. This fusion manifests a symbiotic relationship between aquatic life and plant cultivation, leveraging the strengths of both domains to foster a sustainable food production cycle.
Process and Mechanism
At the heart of aquaponics is a cyclic process where the nutrient-rich water from aquaculture tanks, inhabited by aquatic creatures such as fish or crayfish, nourishes hydroponically grown plants. This cycle is facilitated by nitrifying bacteria that convert the ammonia, a by-product of fish metabolism and potentially toxic in high concentrations, into nourishing nitrates that serve as a nutrient powerhouse for plants.
Sustainable Benefits
Aquaponics epitomises the essence of symbiotic relationships, wherein the aquatic excreta serve as a nutrient base for the plants. This closed-loop system minimises waste, optimises resource usage, and fosters an environment of ecological sustainability and biodiversity.
Conclusion: Towards a Sustainable Future
In conclusion, both permaculture and aquaponics stand as pillars of sustainable practices that work in harmony with nature rather than against it. These approaches envision a future where food production and land management are synonymous with biodiversity, ecological balance, and environmental well-being. As we navigate the path towards a greener future, these practices light the way, showcasing the immense potential of sustainable innovations in nurturing a thriving ecosystem for generations to come.